Modern medicine allows successful prevention and treatment of allergies even during pregnancy. But all this is possible only in the case of a responsible attitude of the woman herself, for the implementation of medical prescriptions, as well as great attention to the state of her health. Competent selection of drugs during pregnancy occurs, without fail, taking into account the duration of pregnancy.
Pregnancy can have a direct impact on the functioning of the immune system, and therefore on the course of allergic diseases themselves. In general, the following trends in the development of allergy symptoms during pregnancy can be distinguished:
- Allergy proceeds in the usual way for this patient;
- Allergic symptoms decrease when pregnancy occurs;
- Allergic symptoms intensify with the onset of pregnancy;
- Allergy disappears during pregnancy;
- Allergic reactions first appear during pregnancy.
Pregnancy itself often provokes allergy symptoms, since at this moment the activity of the woman's immune system is extremely high. So, often women observe spontaneous manifestations of allergic reactions to things familiar to them: cosmetics, food, dust, etc. During pregnancy, it is not recommended to try new products, abuse cosmetics and household chemicals, and is also under intense exposure to sunlight. Do wet cleaning as often as possible and avoid the accumulation of stinging insects (especially bees, wasps, bumblebees and the like), the bites of these insects have very serious consequences.
Allergy symptoms during pregnancy
During pregnancy, allergies manifest themselves with the same symptoms as in the normal state. Allergy symptoms include the following groups:
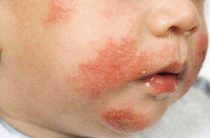
- Skin forms of allergies include various types of inflammation, rashes, changes in the colors and texture of the skin. Often there is redness, drying, swelling of the skin, peeling. In places where allergic reactions appear, there is often severe itching.
- Respiratory forms, which are most characteristic of allergies to dust, flowering plants, components of perfumes and other chemicals. It is characterized by: sneezing, nasal congestion, runny nose, swelling of the nasopharynx, abundant secretion of clear mucus.
- Ocular manifestations of allergy affect the mucous membranes of the eyes and the space around them: redness of the eyes, due to vasodilation, discomfort inside the eye, increased sensitivity to light, tearing, inflammatory reactions.
- Asthmatic phenomena, which are the classic symptoms of bronchial asthma, the most severe of which is the narrowing of the bronchi caused by the ingress of an allergen and provoking suffocation.
- Anaphylactic shock is an extremely severe allergic manifestation that directly threatens the life of the patient. The first symptoms are expressed by a sharp weakness, a feeling of pressure in the chest, an allergic rash may appear, which occurs instantly and covers the entire body in seconds, the whole body seems to burst into flames, the patient turns pale sharply, covered with cold sweat. In the most severe cases, cardiac arrest develops.
Diagnosis of an allergic reaction
Although, for an allergic reaction, the development of symptoms as a result of an allergen is characteristic. In this case, it is often easy to track the dependence of the occurrence of an allergic reaction on the intake of a particular allergen. But, unfortunately, this is not always the case. In some cases, it is impossible to accurately track the culprit of the allergy; in such cases, special diagnostic measures are taken, the nature of which is significantly affected by the state of pregnancy.
Skin tests and provocative tests are not performed during pregnancy, as they involve direct contact for the patient with the allergen. This can cause severe exacerbations of the allergic reaction, which can adversely affect the development of the fetus, even if successfully eliminated.
The only reasonable application of these diagnostic measures is the identification of possible allergens during pregnancy planning. This is recommended for those who have allergies in their family, since the likelihood of an allergic predisposition is extremely high.
Antibody test
A blood test for the presence of antibodies allows you to eliminate the causal relationship between the ingestion of the allergen. Why is it important to know about the presence of antibodies in terms of diagnosing allergies? Antibodies are special protein structures that are designed to signal the arrival of certain adverse agents. With an allergic reaction, their level rises sharply after contact with the allergen.
Elimination diagnostics
Elimination in the diagnostic practice of allergy is the definition of an allergen by the method of elimination. So, for example, when diagnosing food allergies, a gradual rotation of the diet occurs, with the control of one's well-being, depending on the intake of certain products. The elimination method also works for pollen allergies. The patient himself notices that her symptoms occur after the onset of flowering of certain plants, at the same time interval. This practice involves carefully monitoring your well-being, as well as the facts of contact with allergens. The patient needs to carefully look at what surrounds him. If the allergy appeared for the first time, then most likely it arose in response to contact with the factor that you encountered for the first time (new foods, cosmetics, plants, animals).
The effect of allergies on the fetus
And so, first of all, I would like to note that an allergy in a mother affects her child, first of all, by an increased likelihood of transmitting an allergic predisposition to a child by inheritance. The presence of relatives with allergic diseases in the family increases the likelihood of developing allergies in a child. If the allergic person is the mother, then this risk is highest.
By themselves, the allergens with which the mother comes into contact do not affect the child, because they cannot penetrate the fetus, bypassing the placental layer. In addition, it is far from a fact that the child will be allergic to those pathogens from which the mother suffers. If hereditary transmission takes place, then the very nature of the paradoxical immune response is transmitted, but not the causative agent of allergy.
Such severe complications as anaphylactic shock, Quincke's edema or bronchial asthma are accompanied by respiratory depression, which can be fraught with negative changes in the nutrition of the fetus, which lead to oxygen starvation.
Treatment of allergies in pregnant women
Treatment of allergies during pregnancy should be carried out with particular care, in view of the fact that some drugs used to treat allergies can provoke negative changes in the fetus or disrupt the normal course of pregnancy. The selection of drugs is carried out exclusively by the attending allergist in consultation with your gynecologist. Even for the safest drugs, there is no 100% guarantee that there will be no effect on the fetus. Therefore, when choosing drugs for the treatment of allergies, a thorough analysis of the harm and benefits of treatment is carried out, only after that the drug is prescribed.
Antihistamines
These drugs are widely used to relieve the symptoms of allergies. Their action is based on blocking the cellular response to the stimulation of histamine, which is a hormone that causes allergic reactions. The action of these drugs is best manifested in prevention, because in the future, after the action of histamine, there is an accumulation of other factors in the focus of an allergic reaction, which antihistamines do not affect.
The following side effects are characteristic of antihistamines:
- Depression of the central nervous system, which is manifested by fatigue, lethargy, lethargy, decreased reaction;
- Disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, gastritis and ulcers;
- Nausea and dizziness;
- dry mouth;
- Violation of the cardiovascular system;
- Decreased kidney function
Drugs that are prohibited during pregnancy:
- Pipolfen - prohibited for the treatment of allergies in pregnant women;
- Tavegil - has a teratogenic effect. It is taken only as an emergency aid in the treatment of acute forms of allergies;
- Astemizol - is a toxic substance for the fetus;
- Dimedrol - is not used during pregnancy, because it provokes miscarriages due to hypertonicity of the uterine muscles;
- Terfenadine - causes fetal wasting, is not used in therapy in pregnant women.
Corticosteroid drugs during pregnancy
Corticosteroids (in the aspect of medical preparations) are artificial analogues of the hormone cortisol, which is responsible for relieving the symptoms of allergies and inflammation by suppressing the functions of the immune system. Corticosteroids exist in two forms: systemic (tablets and injections), as well as local (creams, ointments, gels, drops, sprays).
Corticosteroid preparations for topical use, according to current medical information, have a minimal degree of penetration into the general circulation. They are not able to penetrate into the tissues of the fetus, do not lead to degenerative changes in the child and do not disrupt the course of pregnancy.
With corticosteroids for systemic use, everything is much more complicated. There is evidence from studies that indicate that the risk of anomalies in the formation of the face increases 4 times, with the use of corticosteroid preparations for systemic use. There are also the following risks: underdevelopment of the fetus, a violation in the development of the brain, underweight, intrauterine death. Naturally, preference is given to local forms of corticosteroids, which are safer for the fetus. Systemic corticosteroids are used to treat severe forms of allergies (angioedema, anaphylactic shock, asthma attacks).
Immunotherapy during pregnancy
Immunotherapy is a method that reduces the pathological sensitivity of the body to allergens. This is due to the fact that the patient has been in contact with artificially administered small doses of allergens for a long time.
The introduction of allergens is carried out using a syringe, as part of standardized solutions. Isolation of the allergenic component and its precise, minimum dosage minimizes the risk for the patient from contact with the allergen. This method must be carried out before the intended conception, since during pregnancy in no case should the body be exposed to contact with allergens.
Results from immunotherapy come after a few months of constant use of this method. The effect lasts from six months to several years, which depends entirely on the individual characteristics of the organism.
hypoallergenic diet during pregnancy
A hypoallergenic diet is a specific dietary measure that consists in the exclusion of foods that have an increasing effect on allergy symptoms due to their biochemical composition. These include: whole milk, bee products, crustaceans and shellfish, cocoa bean products, coffee, citrus fruits, preserves and marinades, hard cheeses, pineapples, tomatoes and their products. Also, products that show a high risk of developing allergic reactions include various products that include preservatives, synthetic colors and flavor enhancers.
The menu of a pregnant woman with allergies should consist of:
Grains are a high quality source of healthy carbohydrates. Carbohydrates that the body receives from cereals maintain a high level of energy for a long time, without sharp peaks and drops, which are typical for fast carbohydrates (white flour products, sweets).
Meat and poultry - preference should be given to lean varieties and parts of the carcass. Preferences must be given: chicken, lamb, rabbit, beef, veal. When properly included in the diet, meat is a highly valuable source of protein, vitamins and minerals.
Vegetables and fruits are a high-quality source of vitamins and minerals, as well as fiber, which is necessary for the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Fermented milk products - the probiotics included in their composition contribute to the reproduction of beneficial intestinal microflora.
Vegetable oils - use them to get "healthy" fatty acids that are involved in numerous vital functions of the body. Supports healthy nails, skin and hair.