Medical studies that have been carried out in recent years have made it possible to determine that one percent of the entire population is susceptible to gluten allergies. This high-molecular protein, which is found in certain cereal cultures, most often causes allergic reactions in infants from six months to 1 year, or in adults from thirty to forty years.
Allergies can develop immediately after ingestion of a food containing gluten, or after several hours or even weeks.
The main symptoms of a gluten allergy in a child are:
- Dyspeptic failures, in which the stool can be with foam and a pronounced odor;
- Irritability, fatigue, drowsiness;
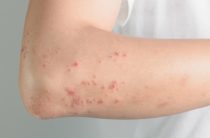
- The appearance of rashes on various parts of the body, which later become dermatitis. The most common locations for the rash are the elbows, knees, scalp, buttocks;
- The child's body weight decreases, the bones are very clearly visible;
- Anemia, which is caused by a violation of the function of blood formation. Hemoglobin is produced in insufficient quantities and therefore the skin is very pale with a yellowish tinge.
If gluten allergy is not treated, developmental delay may occur in older children. It will manifest itself in the difficulty for the child to concentrate and absorb the necessary information. When the disease develops at an older age, the symptoms can vary significantly. So, the disease is supplemented by one symptom or a couple of mild ones, and therefore it is difficult to diagnose it in a short period.
You can make an assumption about the presence of allergies, noticing the following symptoms:
- Constant discomfort in the intestinal area, the pain is not sharp, but aching. It may last a month or even longer;
- Flatulence and a constant feeling of heaviness in the abdomen;
- Chronic liquid stool;
- Rapid fatigue, constant feeling of fatigue;
- Rapid weight loss;
- Pain in muscles, bones, migraine;
- Violation of the normal functioning of the peripheral nervous system, a tingling sensation in the fingers, and after their numbness;
- Dryness in the throat.
Symptoms can appear in a variety of ways. So, they distinguish typical, atypical, latent celiac disease.
The first appears after one to two months after a gluten-containing product was introduced into the child's diet. At eight to nine months, the first allergy symptoms begin to appear. The classic symptoms of such an allergy are:
- significant weight loss;
- bloating;
- aggressiveness, irritability;
- apathy, loss of interest in what is happening;
- loss of appetite;
- joint pain;
- the appearance of caries;
- fainting;
- bleeding.
Such a disease can develop later, when the child reaches the age of two. Symptoms will not be as pronounced, and may not attract the attention of parents for a long time. Atypical celiac disease is considered monosymptomatic. Its main symptom is anemia. Due to the fact that such a symptom is characteristic of many diseases, it is rather difficult to determine it.
Latent celiac disease can only be determined by conducting special studies. For the carrier of the disease, it does not pose a danger, but it can be transmitted genetically. There may be other signs of a gluten allergy. With the development of the disease, a large number of organs are disrupted, and therefore various clinical signs of the disease occur.
What is gluten and why does it provoke allergies?
Gluten or gluten is a protein that is found in large quantities in baked goods, pasta, confectionery, and beer.
Certain types of food are saturated with gluten artificially to give them elasticity. When such food enters the digestive tract, gluten breaks down into fractions, one of them is gliadin. The immune system of weakened people considers such a fraction as a foreign body. When such a protein enters the body, special immune complexes begin to be produced that damage the walls of the small intestine.
In the small intestine, inflammatory processes occur, they provoke atrophy of the mucous layer, and a failure in the normal functioning of the organ. Thus, nutrients are not normally absorbed, they are converted into decay products that poison the body. Gluten allergy has a negative impact not only on the digestive system, but also on the kidneys, cardiovascular system, brain, and endocrine system.
There are two forms of gluten allergy:
- a temporary allergic reaction that occurs in infants after the first complementary foods have begun. When the gastrointestinal tract has matured tightly and the necessary enzymes and bifidobacteria have populated it, allergies can gradually disappear at preschool or school age.
- celiac disease, which can occur due to the fact that the body lacks a certain enzyme that must be used to process gluten. Due to the fact that, when it decays, it releases ammonia, severe symptoms of intoxication occur.
Causes of an Allergic Reaction to Gluten
Celiac disease is considered a hereditary disease, although its gene has not yet been found. But at the same time, it is impossible to say with absolute certainty that parents with celiac disease will definitely pass it on to their child.
Temporary gluten allergy in infants is provoked by early complementary foods and the choice of foods that contain it in large quantities. A breastfed baby does not suffer from gluten allergy because mother's milk does not contain this protein. Complementary feeding with corn, buckwheat, rice porridge should be started from 6 months. These cultures do not contain gluten, they are easily and completely digested in the intestines, even if it is still functioning normally.
After a while, the child’s body produces the enzymes necessary for digestion, the intestines are populated with the necessary lactobacilli, and therefore other cereals begin to be digested normally. Adults may not feel celiac in any way for a long time. After all, very often people mistake colic, gas formation, fatigue for symptoms of other diseases.
A sudden exacerbation of the disease can cause:
- Increased mental stress and stress;
- alcohol abuse;
- Autoimmune pathologies (type 1 diabetes, Down's syndrome, hashimot's disease).
Older children are especially prone to gluten allergies after they have had severe intestinal infections, colds, and have taken antibiotics for a long time.
That is, any disruption in the normal functioning of the intestines can lead to the fact that gluten will no longer be absorbed normally.
Risk of late diagnosis
Due to the fact that the diagnosis is established very late, serious changes can occur in the human body that are difficult to correct. So, when a patient with celiac disease grows more slowly than his peers. Having made a diagnosis at one or two years and having begun the necessary treatment, the child will not lag behind the same age. Timely diagnosis ensures the child's quick return to normal life, normal growth and development.
The child will have good psychological and physical health, sexual development. While in patients secondary changes begin to appear, which are quite problematic to correct. As for the issue of failures in the intrauterine development of the child of the mother who suffers from gluten allergy, it is worth noting that there is no direct connection between them. Pregnant women who adhered to a gluten-free diet, were treated with drugs prescribed by the doctor, gave birth to children who did not have health problems.
How is gluten allergy treated?
When the doctor suspects that you or your child is allergic to gluten, special tests are prescribed to confirm the diagnosis - skin tests. In the future, according to their results, treatment and diet are selected. When the first signs of a gluten allergy appear in a baby, it is necessary to change his diet.
By choosing gluten-free foods such as corn, buckwheat, rice, meat, cottage cheese, potatoes, legumes, fish, you can avoid the development of allergic reactions. The expansion of the diet can be carried out as the baby grows up, constantly monitoring his well-being.
Semolina, oatmeal, wheat porridge, pearl barley, barley groats contain a lot of protein, and therefore dishes from them are prepared for children who have reached the age of two.
It is best to eat baked goods made from corn or buckwheat flour, since wheat flour also contains an allergen.
Moms should carefully read the composition of purees and cereals that are sold in jars and may contain this protein. After the child's menu becomes correct, does not contain an allergen, the signs of the disease will begin to disappear. A doctor may prescribe a medical course of therapy, which includes the use of enterosorbents, antihistamines, anti-inflammatory ointments and creams, drugs that regulate bowel function.
Thus, the baby's body will be able to recover in the shortest possible time.
It is forbidden to eat:
- Dishes that contain oats, barley, wheat, rye;
- Flour products (bread, pasta, pastries, cakes);
- Whole milk and yogurt;
- Seasonings and hot sauces;
- Pickled and canned foods;
- Offal (liver, kidneys, lungs) and products from them
(sausages, sausages).
Many products contain gluten, so be sure to check the ingredients before buying. This protein can be found not only in food, but also in cosmetics, or even envelope glue. Gluten allergy should not be considered a sentence, you can fully live with it. In young children, such a disease may not occur, subject to the correct introduction of complementary foods and normal nutrition.
We advise you to read: