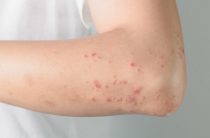
Urticaria is a disorder that has an allergic origin and is expressed as a profuse specific rash of the skin. The formation of this disease can occur in acute or chronic form. It is the acute form of urticaria that represents the majority of cases for the given disease.
Acute urticaria is quite easily eliminated if measures to interrupt contact with the allergen and the therapeutic effect were made with great haste. How long the symptoms of the disease will be eliminated depends entirely on the severity of the symptoms, as well as on the moment when the treatment was started.
Why does acute urticaria occur?
In the development of urticaria, the main role is played by the susceptibility of the patient's immune system in relation to the established components - allergens. A characteristic feature of allergens is that they are not harmful (like, for example, poisons or parasites) and can cause negative reactions only in certain patients. After they have penetrated, a reaction from the immune system begins. Having sensitivity to this substance, the patient's body secretes special antibodies that stimulate the cells of the immune system containing histamine.
In patients with urticaria, histamine causes a number of transformations in the tissues of the upper layers of the skin. In the course of its action, the expansion of capillaries occurs. As a result of these processes, redness, swelling of the skin and accumulation of fluid in places of inflammatory processes are produced. The patient notices this as a collection of red rounded rashes. In acute urticaria, the production of antibodies occurs very quickly, as a result of which the reactions of this disease are shown almost instantly. In addition to affecting the blood vessels, substances that contribute to the occurrence of allergic reactions also stimulate nerve fibers, which are present in abundance in skin tissues. As a result, the patient feels that the skin is very itchy. With urticaria, this sensation is so unpleasant that it can be the basis for sleep disturbance and even nervous disorders.
The acute form of the disorder can develop in response to the ingestion of various substances or exposure to factors. But on the basis of medical statistics, it was possible to identify the most frequent provocateurs of this disease.
They belong to:
- medicines (antibiotics, anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs);
- venom of ants, wasps, hornets, bumblebees, bees;
- thermal effects (overheating, hypothermia, sunlight);
- substances contained in cosmetics, perfumes and household chemicals;
- hair and excretions of animals (if it comes into contact with the skin or inside);
- food allergies (chocolate, nuts, seafood, berries, citrus fruits);
In addition to factors of an external nature, the disease can develop as a result of emotional disorders. Poor sleep, various stresses, nervous tension can also contribute to the appearance of this disease.
Main symptoms
The appearance of acute urticaria on the skin occurs at lightning speed. There are no signs that could indicate its occurrence in the near future. This disease is characterized by the appearance of a rash, which is represented by round, barely noticeable raised formations of bright red or vice versa pink color. The skin, which is affected by inflammatory processes, is very itchy. During the acute form of urticaria, its symptoms appear almost instantly, rarely taking more than a few hours. In this case, the rash is characterized by a high degree of saturation, covering large areas of the skin.
These formations can be identified in different ways. It can be frequent accumulations of small rashes, or vice versa, large continuous areas of inflammation. During acute urticaria, an increase in body temperature can also be observed, which is accompanied by a feeling of cold, aching in the back and limbs. Unlike other skin manifestations, acute urticaria passes without a trace, leaving no scars on the skin.
Diagnosis of acute urticaria
Determining the cause of acute urticaria is much easier than chronic. This is due to the fact that a small time period that has passed since the moment of contact allows you to more accurately track the relationship between exposure to the allergen and the symptoms of malaise. Of fundamental importance, in addition to the actual allergic nature of the disease, is also an indication of the allergen that provokes it.
For diagnosis, appropriate measures and analyzes are used:
- skin tests (application of suspected allergens to the skin using various medical devices);
- laboratory examination of the skin;
- general and special blood test for antibodies;
- Analysis of urine.
Food allergies are often the cause of acute urticaria. In this case, the doctor draws up a list of potential allergens, based on a detailed questioning about the patient's diet. Then, within two weeks, the patient is transferred to a diet of non-allergenic food. After this period, the introduction of the alleged allergens and the observation of skin reactions takes place. Such diagnostic methods require direct entry of the allergen into the body, therefore, they should be carried out only under the supervision of specialists in compliance with all the required precautions.
Treatment of acute urticaria
The key to successful treatment of acute urticaria is the elimination of contact with the allergen. Specific measures may vary, depending on the nature of the allergen. So, if the urticaria is caused by the penetration of allergens contained in the secretions of pets, then they should be given into safe hands, and the house should be thoroughly cleaned. If the symptoms of the acute form are associated with food allergens, then sorbents are used to remove them as soon as possible. In case of drug intolerance, a drug that does not provoke allergic reactions is selected. An enema or gastric lavage may also be involved.
After measures have been taken to eliminate contact with the allergen, drug treatment is started. Its purpose is to relieve the symptoms of malaise. Antihistamines are definitely used. They block the effect of histamine, which is a hormone that provokes hives and a number of other allergic reactions. Such drugs as tavegil, diazolin, diphenhydramine, suprastin lead to increased inhibition of the nervous system. This is expressed as a feeling of weakness, drowsiness, affects the decrease in physical and intellectual performance. New antihistamines (claritin, cestin, erius, tsetrin, etc.). are deprived of this unpleasant feature, therefore, in the treatment they are more preferable means.
Antihistamines do not always contribute to the complete elimination of the symptoms of the disease, since other mechanisms of its development may be involved in the formation of acute urticaria. Therefore, corticosteroid injections may be prescribed. They try not to use these drugs for more than five days in order to avoid their harmful effects on the body.
During the course of this disease, there is an intense accumulation of fluid in the tissues, so diuretics are often used. Although they do not directly affect the mechanisms of allergy development, they nevertheless significantly alleviate the symptoms.