With food allergies, it is often difficult to determine on your own which food to exclude from the diet. This is due to a special mechanism for the development of food reactions, which occurs rather slowly. So, for example, the symptoms of allergic diseases can be manifested 3-5 days after the ingestion of a substance that provokes it. Therefore, tests for food allergens play an important role in the diagnosis of this disease.
When diagnosing a food allergic reaction, it is important to distinguish it from individual forms of food intolerance, since these are completely different pathological processes. Food allergies are caused directly by an allergen, that is, a substance that, when ingested, causes an acute reaction from the immune system. While the deterioration of the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, with poor absorption of lactose is not allergic, since it is not caused by lactose, as an allergen, but by a lack of enzymes that are responsible for its absorption.
The actual reaction of an allergy to food occurs according to the following mechanism: in response to an allergen, an organism that has previously been in contact with this substance and has a corresponding predisposition produces antibodies. The further development of an allergic reaction depends on the effect of the allergen on the corresponding mast cell receptors.
Why does the body of certain people perceive the same food as an irritant, while others are tolerated normally? The answer to this question lies in the development of a certain predisposition, to the sensitivity of the immune system in relation to certain components of the products. This predisposition can be either hereditary or acquired.
The presence of a substance that provokes an allergy in the food consumed by the patient is a prerequisite for the development of allergic reactions. After digestion of food by the gastrointestinal tract, sensitive immune cells diagnose its presence and begin to produce antibodies that are able to combine with a specific allergen. Further, antibodies affect the surface of mast cells, in which the corresponding chemical transformations occur, as a result of which the membrane opens and releases histamine into the blood, which is involved in the development of symptoms of allergic reactions.
Specific symptoms from exposure to a provoking agent may vary, depending on the ratio of mast cells in a patient in certain tissues. For example, if a large number of mast cells are localized in the epidermis, then when a provocative substance enters, a sore throat, swelling in the larynx, and a dry cough develop. If mast cells are predominantly located within the intestines, then disorders of the gastrointestinal tract can occur.
Food allergens have the following features: they must be substances of a protein nature that are resistant to enzymatic processing, as well as to the influence of an acidic environment. These substances from food enter the blood, retaining their protein structure and entering the blood unchanged, so that they remain complementary to antibodies. The nature of the product, and specifically the speed of its digestion, after which the allergen enters the bloodstream, also affects the rate of development of an allergic reaction.
Clinical laboratory tests
When an allergen enters, patients often experience a phenomenon such as eosinophilia. Eosinophilia is an increased concentration of eosinophils in the body. These cells are involved in the production of antibodies that react to the penetration of allergens. Laboratory blood samples from peripheral tissues diagnose an increase in the concentration of eosinophils, within 15%. If food allergy occurs with rhino-conjunctival symptoms, which is quite rare. However, when diagnosing nasal or conjunctival discharge, it is often possible to notice an increase in the level of eosinophils from 5 to 80%, in relation to normal values.
Provocative tests for allergies
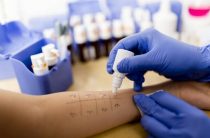
Provocative tests, for food allergies, are one of the most effective tests to establish the effect of a suspected substance on the body. These methods are carried out only in a hospital, where it will be possible to provide special medical care in case of complications.
The oral method of introducing the allergen will be the most effective, due to the specificity of the mechanisms for the development of food allergies. Some chemical variations of the allergen can only occur during transformation in the gastrointestinal tract. While unchanged, the allergen may not pose a danger, which will directly affect the test results.
For direct carrying out of this analysis, a food allergen concentrate is used, enclosed in a special capsule of a soluble substance. The standard allergen dose is 8 mg. Control diagnostics is carried out 48 hours after the introduction of the allergen. The dosage is increased if the allergy symptoms are not confirmed, but there is a strong reason to believe that the patient is allergic to this particular product. The threshold dosage, when conducting this analysis, is 8000 mg.
Conditions for conducting provocative tests:
- It is mandatory to carry out, on an empty stomach, in the morning;
- The patient's well-being should not differ from the usual state;
- The patient is monitored for 48 hours;
- Precautions are taken to deal with severe complications;
- Increasing the dosage of the allergen occurs gradually;
- In addition to special symptoms, blood pressure, heart rate and strength, blood glucose levels and other standard indicators are diagnosed;
- Not performed with those allergens that cause acute development of severe symptoms
Another type of provocative methods used in allergy testing is skin tests. The problem is that allergy in the presence of a food allergen develops using the mechanism of IgM antibodies, which are involved in the development of delayed-type reactions. These reactions very rarely develop with the introduction of an allergen into the skin. Therefore, these tests for food allergies are very rare.
Special blood test for food allergies
During a blood test, with food allergies, the level of general and specific antibodies has a diagnostic value. Specific antibodies are responsible for the occurrence of allergic reactions that develop in a delayed manner. While the level of common antibodies that are responsible for the instantaneous symptoms of allergies (allergic rhinitis, conjunctivitis, bronchial asthma) is quite rare with food allergies, since such reactions are quite rare for this type of allergy.
These samples are safe because the blood material that is removed from the patient comes into contact with the allergen in the laboratory. After the reaction, the diagnosis of the level of antibodies begins. Their increase is a confirmation that this substance is the cause of the disease for this patient.
A blood test for the level of antibodies can, in contrast to provocative methods for determining allergens, also be carried out for pregnant women, young children and people who are in a state of exacerbation of allergy symptoms, in which the use of provocative tests can cause undesirable consequences.